If you’re in waste tire recycling but are stuck “only selling low-priced crumbs” with “paper-thin profits”; or want to enter the circular economy but don’t know “where to start most safely”—this article will explain how tire rubber powder plants turn “widely discarded waste tires” into “high-demand materials for roads and playgrounds”, as well as the full process details of setting up a plant.
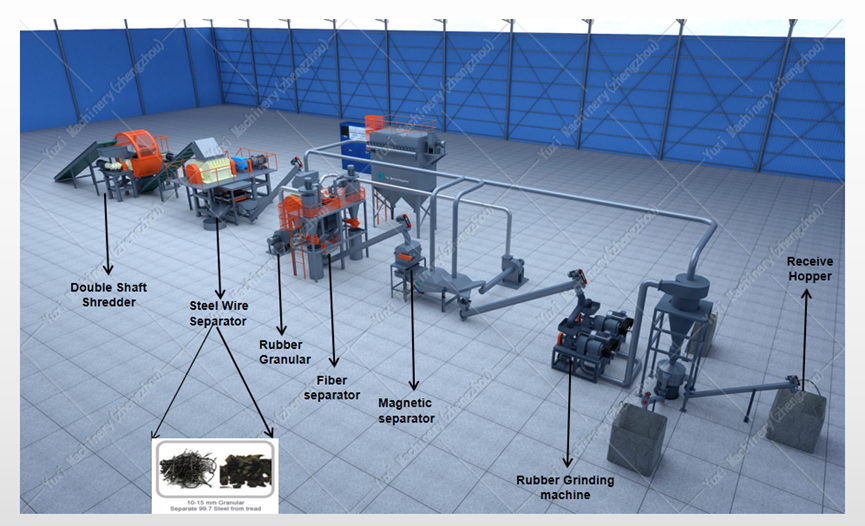
I. First, Understand: The “Golden Position” of Tire Rubber Powder Plants in the Industry Chain
Waste tire recycling is not a “one-time deal”; it is divided into 3 links:
- Link 1: Tire Collection → Rough Shredding: Recyclers cut tires into “steel-containing large blocks” and sell them to crumb plants, with a profit of about 50-100 yuan/ton;
- Link 2: Crumbs → Steel Removal: Crumb plants turn large blocks into “steel-free rubber crumbs” and sell them to rubber powder plants, with a profit of about 100-200 yuan/ton;
- Link 3: Crumbs → Rubber Powder: Rubber powder plants grind crumbs into “high-purity rubber powder” and sell it to end customers, with a profit of about 800-1200 yuan/ton;
As you can see, rubber powder plants are the “profit endpoint” of the industry chain—the previous links earn “hard money”, while only rubber powder plants earn “money from technology and value”.
II. 11 Processes + Hidden Details of Tire Rubber Powder Plants
Many people think “grinding powder is just putting crumbs into a machine”, but truly producing “99.9% purity” rubber powder relies on “detail work” in 11 processes:
Bead Pretreatment: Replace “Manual Prying” with “Hydraulic Cutting”
- Use a hydraulic bead cutter to “cut and peel off” the steel bead at the edge of the tire, which is 10 times more efficient than manual prying and avoids steel residue;
- The peeled steel bead can be sold separately for “3000 yuan/ton”, earning an extra 500 yuan/ton compared to mixing it in crumbs.
Tire Cutting: “Rotary Cutting” Saves 30% Electricity Compared to “Linear Cutting”
- Use a rotary tire cutter to cut the whole tire into 4-5 pieces; the tire “rotates automatically” during cutting, resulting in more uniform force;
- Only 20 kWh of electricity is needed to cut 1 ton of tires, saving 30% compared to linear cutters.
Primary Shredding: “Dual-Shaft Opposed Cutting” Makes Crumbs More Uniform
- Use a dual-shaft shredder (50mm blade spacing) to cut tire blocks into 50mm rubber blocks; the blades are made of “Cr12MoV alloy steel” and can process 1000 tons of tires before replacement;
- Spray “atomized water” to cool down during shredding to prevent rubber from “sticking to blades” due to high temperature, increasing product qualification rate by 5%.
Secondary Shredding: “Hammering Type” Turns Blocks into “Granules”
- Use a hammering shredder to turn 50mm rubber blocks into 10-20mm rubber granules; the hammer head uses a “replaceable wear-resistant layer”, reducing maintenance costs by 60% compared to replacing the entire hammer head;
- The equipment has a built-in “screen”, and unqualified large granules are “automatically returned”, achieving 100% raw material utilization.
Primary Magnetic Separation: “Drum Magnetic Separation” Absorbs 3% More Steel Than “Suspension Type”
- Use a drum magnetic separator (12000 Gauss magnetic field strength) to absorb residual steel in rubber granules, with a separation rate of 97%;
- The magnetic separation drum is “covered with stainless steel” to prevent rubber granules from “being adsorbed on the drum”, increasing processing efficiency by 20%.
Tertiary Grinding: “Impact Type” Makes Granules Finer
- Use an impact grinder to grind 10-20mm rubber granules into 1-0mm rubber particles; the grinding chamber is “lined with ceramics” to avoid contaminating the rubber;
- Use “air and water cooling dual temperature control” during grinding to keep the rubber temperature ≤40℃ and ensure performance does not degrade.
Secondary Magnetic Separation: “High-Gradient Magnetic Separation” Captures “Micron-Level Steel”
- Use a high-gradient magnetic separator to separate steel again, with a separation rate of 99%, even “micron-level steel debris” can be absorbed;
- The rubber particles after magnetic separation “have no visible steel wire” and can directly connect with “high-requirement customers”.
Vibratory Classification: “4-Layer Screen” Divides into 6 Specifications
- Use a 4-layer vibratory classification screen to divide rubber particles into 6 specifications: 0-1mm, 1-3mm, 3-5mm, 5-8mm, 8-10mm, 10-15mm;
- The screen can be “quickly replaced”, and switching specifications only takes 10 minutes, meeting the “customized needs” of different customers.
Return Material Circulation: “Negative Pressure Conveying” Sends Large Granules Back to Grinding
- Use a negative pressure conveying system to send the large granules screened out back to the tertiary grinder, avoiding manual handling and saving 2 laborers;
- The conveying pipeline is “lined with wear-resistant rubber” and has a service life 3 times longer than ordinary pipelines.
Fiber Separation: “Airflow + Static Electricity” Dual Separation
- Use an airflow static fiber separator to separate residual fiber from rubber powder, with a fiber removal rate of 99%;
- The separated fiber has “moisture content ≤10%” and can be directly sold to “biomass fuel plants” for 200 yuan/ton.
Fine Grinding: “Colloid Mill” Produces “140-Mesh Fine Powder”
- Use a colloid mill to grind rubber particles into 10-140 mesh rubber powder, with a grinding gap “precise to 0.01mm”;
- The ground fine powder “feels like flour” and can be used in high-end scenarios such as “baby crawling mats” and “medical rubber products”.
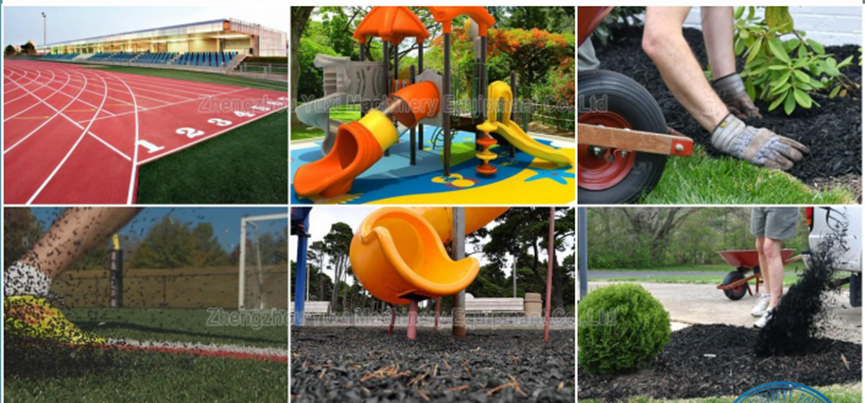

III. 6 High-Value End Applications + Customer Development Tips for Tire Rubber Powder
The profit of rubber powder depends on “which customers you can connect with”—the profit difference between different applications can reach 10 times:
High-Grade Highways: “Rubber Asphalt” Is “A Must-Have”
- Demand: 10-15 tons of rubber powder are needed per kilometer of expressway, which can extend the road life by 30%;
- Development Tips: Cooperate with local “Highway Bureau” and “Asphalt Mixing Plants”, and provide “third-party test reports” to prove that the rubber powder meets the Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements;
- Profit: 1800-2200 yuan/ton, with an annual demand of over 1000 tons.
Sports Facilities: “Plastic Runways” Are “Profit High Grounds”
- Demand: 3-5kg of rubber powder are needed per square meter of plastic runway, and schools, gymnasiums, and parks are all building or renovating;
- Development Tips: Cooperate with “Sports Facility Engineering Companies” and provide “environmental test reports” (free of heavy metals and VOCs);
- Profit: 2000-2800 yuan/ton, and a standard playground can use 50-100 tons.
Auto Parts: “Seals and Shock Absorbers” Are “Long-Term Orders”
- Demand: Automobile factories need “high-purity rubber powder” for seals and shock absorbers, requiring “uniform particle size and no impurities”;
- Development Tips: Send “sample tests” to auto parts factories, and obtain “annual framework orders” after passing;
- Profit: 2500-3000 yuan/ton, and a medium-sized parts factory has an annual demand of over 500 tons.
Building Waterproofing: “Rubber Membranes” Are “Policy Dividends”
- Demand: New buildings need “rubber waterproof membranes”, and the state requires “green building materials to account for ≥30%”;
- Development Tips: Cooperate with “Waterproof Material Factories” and provide “RoHS certification” (EU environmental protection standard);
- Profit: 1900-2300 yuan/ton, with an annual demand of over 800 tons.
Shoe Sole Materials: “EVA Rubber Composite Soles” Are “Consumption Upgrade”
- Demand: Sports shoe factories need “fine rubber powder” for EVA composite soles, requiring “100-140 mesh and 99.9% purity”;
- Development Tips: Cooperate with “Shoe Material Traders” and provide “yellowing resistance test reports”;
- Profit: 3000-3500 yuan/ton, and a small shoe factory has an annual demand of over 300 tons.
Biomass Fuel: “Rubber-Derived Fuel” Is “Bottom Guarantee”
- Demand: Cement factories and power plants need “high-calorific-value fuel”, and the calorific value of rubber-derived fuel is 20% higher than that of coal;
- Development Tips: Cooperate with “Fuel Distributors” and provide “calorific value test reports” (≥4200 kcal/kg);
- Profit: 1500-1800 yuan/ton, which can digest “unqualified rubber powder” and ensure the factory “does not lose money”.


IV. 3 Sizes + Investment Returns of Tire Rubber Powder Plants
Depending on your capital and resources, rubber powder plants can be divided into 3 sizes:
Small-Scale Plant: 10 Tons/Day Processing Capacity
- Investment: 200,000-300,000 yuan for equipment + 500㎡ of space (50,000-80,000 yuan/year rent) + 100,000-150,000 yuan for environmental assessment, with a total investment of about 500,000-600,000 yuan;
- Profit: 800-1000 yuan profit per ton, annual profit of about 240,000-300,000 yuan, payback in 2 years;
- Suitable For: Small recyclers with stable crumb sources who want to “test the waters in small steps”.
Medium-Scale Plant: 30 Tons/Day Processing Capacity
- Investment: 500,000-700,000 yuan for equipment + 1000㎡ of space (100,000-150,000 yuan/year rent) + 200,000-250,000 yuan for environmental assessment, with a total investment of about 1,000,000-1,200,000 yuan;
- Profit: 1000-1200 yuan profit per ton, annual profit of about 900,000-1,080,000 yuan, payback in 1.5 years;
- Suitable For: Entrepreneurs with resources to connect with highways and sports facilities who want to “profit on a large scale”.
Large-Scale Plant: 100 Tons/Day Processing Capacity
- Investment: 1,500,000-2,000,000 yuan for equipment + 3000㎡ of space (200,000-300,000 yuan/year rent) + 300,000-400,000 yuan for environmental assessment, with a total investment of about 2,500,000-3,000,000 yuan;
- Profit: 1200-1500 yuan profit per ton, annual profit of about 4,320,000-5,400,000 yuan, payback in 1 year;
- Suitable For: Enterprises with industry chain resources who want to “become regional leaders”.

V. 5 Pitfall-Avoidance Tips for Setting Up a Tire Rubber Powder Plant
Do Not Buy “Used Equipment”
- The “blades and bearings” of used equipment are already worn, which not only has a high failure rate but also affects product quality;
- New equipment has a “1-year warranty”, and suppliers provide “free commissioning + training”, which is more worry-free than used equipment.
Do Not “Blindly Pursue Fine Powder”
- 140-mesh fine powder has high profits, but grinding costs are also high, and market demand is “not that large”;
- First produce “30-80 mesh medium powder” to connect with highway and waterproofing customers, and then expand the fine powder market after stabilization.
Do Not “Rely on Only One Customer”
- Putting “all eggs in one basket” will cause the factory to “shut down” once the customer bargains or terminates cooperation;
- Connect with at least 3-5 customers in different industries to ensure “if one fails, others will work”.
Do Not “Ignore Environmental Protection”
- The dust and noise of rubber powder plants are “key targets of environmental inspection”, and once exceeding standards, you will be “fined + shut down”;
- Be sure to “do environmental assessment” before commissioning, and equip with “baghouse dust collector + sound insulation room”, do not “get on the bus first and then buy a ticket”.
Do Not “Stock Too Much Inventory”
- The “shelf life of rubber powder is 2 years”, but market prices fluctuate, and too much inventory will “occupy funds + bear price drop risks”;
- Adopt the “produce-to-order” model, and produce after customers place orders, controlling inventory at “3-5 days of supply”.
VI. Conclusion: Tire Rubber Powder Plants Are the “Ultimate Choice” for Waste Tire Recycling
If you want to change from a “recycler earning hard money” to a “factory owner earning technology money”, tire rubber powder plants are the “most stable springboard”—you don’t need to “collect tires all over the street”, as long as you connect with “crumb plants” and “end customers”, you can “stably earn profits” in the factory.
Moreover, with the promotion of the “dual-carbon policy” and “green building materials”, the demand for rubber powder will only grow—entering now means “grabbing the first wave of dividends”.
